| 【R语言】如何进行英文分词统计(以《爱丽丝漫游奇境》词频统计为例)(20年3月22日复习笔记) | 您所在的位置:网站首页 › r语言 readlines › 【R语言】如何进行英文分词统计(以《爱丽丝漫游奇境》词频统计为例)(20年3月22日复习笔记) |
【R语言】如何进行英文分词统计(以《爱丽丝漫游奇境》词频统计为例)(20年3月22日复习笔记)
|
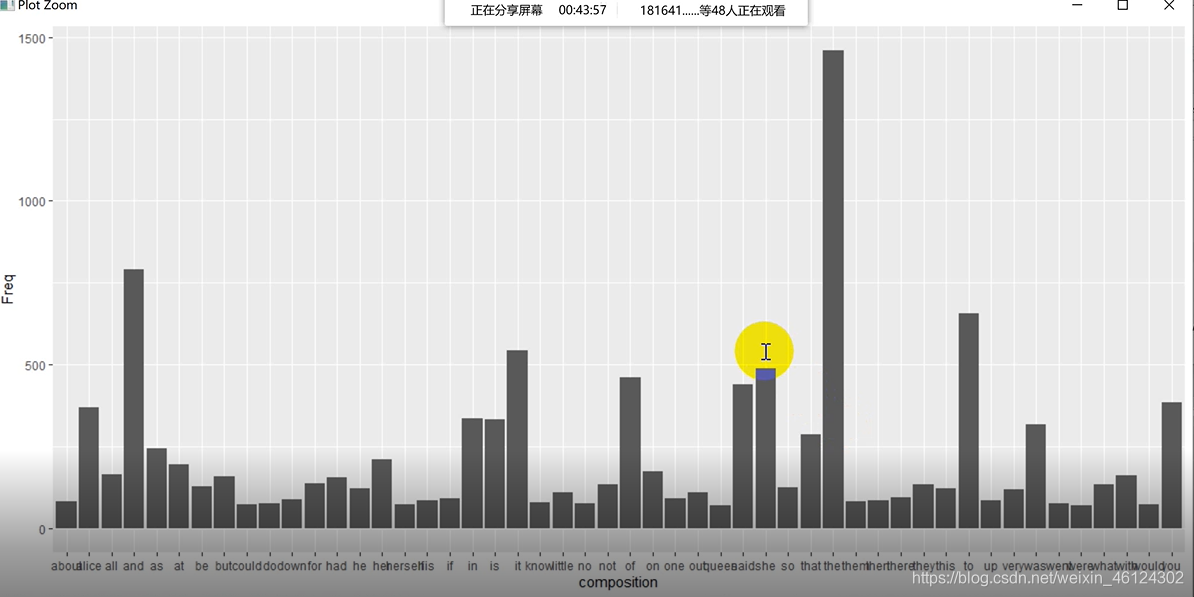
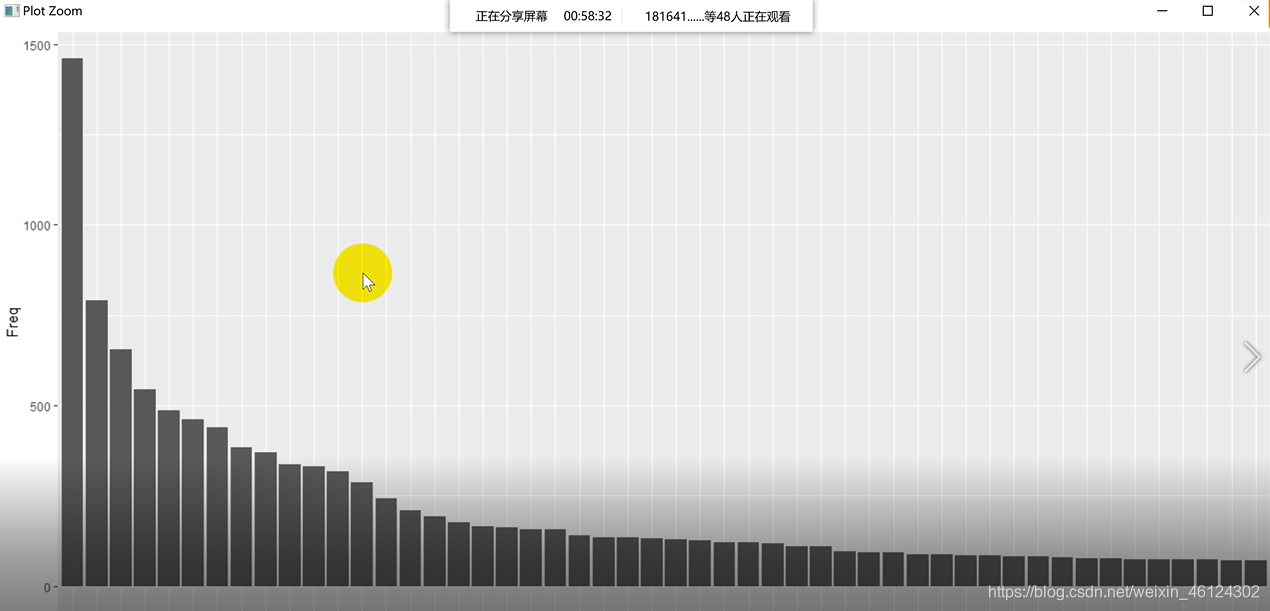
老师所给的题目要求是 其中,老师介绍了两种导入文档的方式,一种是全文读入,一种是逐行读入。先说全文读入的方法 一、全文读入 #法一:全文本读入,用scan扫描文件 txt = scan("Alice's Adventures in Wonderland - Lewis Carroll.txt","") #用意同↓,以字符串格式读入txt #txt = scan("Alice's Adventures in Wonderland - Lewis Carroll.txt",what = "c") txt关于scan读入文档的语句,翔宇亭IT乐园前辈介绍了scan语法的五种例句: (1)scan(“student.txt”, what=“c”) #以字符串的格式读取数据 (2)scan(“student.txt”, what=“c”, nlines=3) #读取3行 (3)scan(“student.txt”, what=“c”, skip=1) #忽略第1行 (4)scan(“student.txt”, what = list(studentNo="", studentName="", studentSex="", studentAge=0), skip=1) #以列表的形式读取数据 (5)lst #确保不是空的文章,异常处理;逐行处理 print(line) line = readLines(con,n = 1) } 运行结果如图 help里说这个函数的n起到的是最大值的作用,最大读到第n行,如果要全部读完需要赋值为负 我比较好奇的是,为什么这个语句里没有n++的描述,但是还是能读完全部文章,而不是疯狂读第一句话呢 这里我先挖个坑,等我整明白了再回来补充 3.大小写处理这个比较简单 temp_line = tolower(line) #全部转化为小写即可 4.特殊字符处理有两种方式处理 (1)使用gsub函数对特殊符号一个一个替换 temp_line = gsub("'s"," is ", temp_line)#把temp_line中的s转化成is temp_line = gsub("'s"," is ", temp_line) temp_line = gsub(";"," ", temp_line) temp_line = gsub(","," ", temp_line) temp_line = gsub("'"," ", temp_line) temp_line = gsub(":"," ", temp_line) temp_line = gsub("-"," ", temp_line) temp_line = gsub("`"," ", temp_line) temp_line = gsub("\n"," ", temp_line) temp_line = gsub('\"'," ", temp_line, fixed = TRUE) temp_line = gsub("?"," ", temp_line, fixed = TRUE) temp_line = gsub("*"," ", temp_line, fixed = TRUE) temp_line = gsub("."," ", temp_line, fixed = TRUE) #要用fixed是因为 #通配符(用于匹配特定字符的符号,这里就把.?\*等字符,默认转化为通配符。 #为了避免使用通配符,必须修复注意,像.?*等字符是通配符,也就是说代表着一些字母或符号,比如"."就是代表全部字母,直接替换会把他们代表的东西全替换了,所以要在fixed属性中设为TRUE fixed logical. If TRUE, pattern is a string to be matched as is. Overrides all conflicting arguments. (2)正则表达式 temp_line = gsub("[^a-zA-Z]"," ",temp_line) #正则表达式表示匹配所有非字母字符 更多正则表达式的匹配,在gearss前辈的博文中有详细的归纳。 5.保存文件 #保存文件,以方便未来使用 out_con = file("processTXT20200322.txt","w")#用w写模式写入保存(这种模式下可以修改文件) write(processed,out_con,ap 6.提取词频 # 重新提取每一个处理好的词 composition = strsplit(x = processsed,split = " ")# 按照空格拆分文本为一个一个的词!注意:这种方法只在英文下生效,中文没有空格,我们必须使用中文分词法 7.建立词频表建立表格 wordsFreq = data.frame(table(composition)) wordsFreq[,1] = as.character(wordsFreq[,1])#为方便后续操作,把第一行的单词转换为字符型建立完表格后,我们会发现,表格中出现了空格和一些没有含义的词 因为我们要找的是前50个频繁词,所以要排一下顺序(前500个同理) wordsFreq = wordsFreq[order(-wordsFreq$Freq),]#从大到小排序然后保留前50个 wordsFreq[1:50,] data = wordsFreq[1:50,]#取前50个保存至此,数据处理的部分就完成了。 三、画图 1.柱状图 ggplot(data = data, aes(x=composition,y=Freq))+geom_bar(stat = "identity")#属性指代XY轴名字和类型(柱状图)结果如图 X轴的文字都挤在一块儿了,可以改成纵向排列的↑ 当然,为了再美观一点,我们也可以再作图使其从大到小排列↓ # 设置柱状条形图的顺序 data$composition = factor(data$composition,levels = c(data$composition)) #设置柱状条形图的顺序 ggplot(data = data, aes(x=composition,y=Freq))+geom_bar(stat = "identity")+theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 90,hjust = 1))
如果有专门的停止词txt的话,也可以加以使用,过滤到诸如"he""she"等无意义词 # 停用词问题 # tm包里面内置的一部分停用词 stopwords = read.table("stopwords.txt",header = FALSE) clean_wordsFreq = wordsFreq for (word in wordsFreq$composition){ if (word %in% stopwords$V1){ clean_wordsFreq = clean_wordsFreq[-which(clean_wordsFreq[,1]==word),] } } data = clean_wordsFreq[1:50,]最后附上完整代码 ################################################### setwd("D://1Study//R//CH 03") getwd() ################################################### library(ggplot2) #library(NLP) #自然语言处理的包 #library(tm) #文本挖掘的包 library(wordcloud2) #绘制词云的包 ##### #1.读取小说 #法一:全文本读入,用scan扫描文件 txt = scan("Alice's Adventures in Wonderland - Lewis Carroll.txt","") #用意同↓,以字符串格式读入txt #txt = scan("Alice's Adventures in Wonderland - Lewis Carroll.txt",what = "c") txt #法一不太好,因为标点符号也会被作为单词读入 #法二:逐行读取,并在读取过程中逐行处理异常文本 processed = ""#用来保存文本 con = file("Alice's Adventures in Wonderland - Lewis Carroll.txt","r") #定义一个变量用于读取文件 line = readLines(con,n = 1) #读取con的第一行 #接下来开始做循环,从第一行往下循环 while (length(line)!=0) {#确保不是空的文章,异常处理;逐行处理 temp_line = tolower(line) #全部转化为小写 temp_line = gsub("'s"," is ", temp_line)#把temp_line中的s转化成is temp_line = gsub("'s"," is ", temp_line) temp_line = gsub(";"," ", temp_line) temp_line = gsub(","," ", temp_line) temp_line = gsub("'"," ", temp_line) temp_line = gsub(":"," ", temp_line) temp_line = gsub("-"," ", temp_line) temp_line = gsub("`"," ", temp_line) temp_line = gsub("\n"," ", temp_line) temp_line = gsub('\"'," ", temp_line, fixed = TRUE) temp_line = gsub("?"," ", temp_line, fixed = TRUE) temp_line = gsub("*"," ", temp_line, fixed = TRUE) temp_line = gsub("."," ", temp_line, fixed = TRUE) #要用fixed是因为 #通配符(用于匹配特定字符的符号,这里就把.?\*等字符,默认转化为通配符。 #为了避免使用通配符,必须修复 processed = paste(processed,temp_line," ")#连接已有内容和新加入行的内容,中间用空格分开 #即↓ #processed = paste(processed,temp_line,sep = " ") processed line = readLines(con,n = 1) } ##### #保存文件,以方便未来使用 out_con = file("processTXT20200322.txt","w")#用w写模式写入保存(这种模式下可以修改文件) write(processed,out_con,append = TRUE)#append表示允许追加 close(out_con)#关闭文件 getwd() ###### # 重新提取每一个处理好的词 composition = strsplit(x = processsed,split = " ")# 按照空格拆分文本为一个一个的词 #!注意:这种方法只在英文下生效,中文没有空格,我们必须使用中文分词法 # 建立频数表 wordsFreq = data.frame(table(composition)) wordsFreq[,1] = as.character(wordsFreq[,1])#为方便后续操作,把第一行的单词转换为字符型 wordsFreq = wordsFreq[-which(nchar(wordsFreq[,1]) clean_wordsFreq = clean_wordsFreq[-which(clean_wordsFreq[,1]==word),] } } data = clean_wordsFreq[1:50,]以上是我对英文分词词频统计的理解,如果表述有误,欢迎批评指正。 |
【本文地址】
 这是一道对英文进行分词的词频统计。 首先当然是要导入这个文档以及所需要的的包(绘制频数图需要ggplot2包,绘制词云需要wordcloud2包)
这是一道对英文进行分词的词频统计。 首先当然是要导入这个文档以及所需要的的包(绘制频数图需要ggplot2包,绘制词云需要wordcloud2包)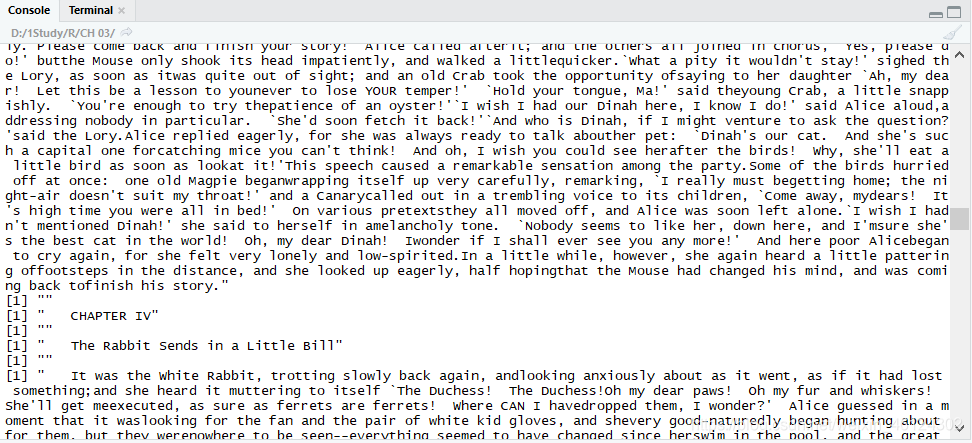 不过对于这一语句,我存在如下疑问
不过对于这一语句,我存在如下疑问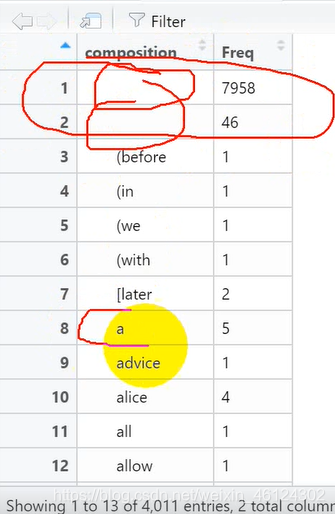 所以我们**用“当单词的长度小于2时,删除该单词”的方法过滤上述词频 **
所以我们**用“当单词的长度小于2时,删除该单词”的方法过滤上述词频 **